vLLM源码(V0)结构分析
vLLM使用通常如下(本地推理,非服务):
from vllm import LLM
llm = LLM(model="facebook/opt-125m")
outputs = llm.generate("Hello, my name is")
for output in outputs:
prompt = output.prompt
generated_text = output.outputs[0].text
print(f"Prompt: {prompt!r}, Generated text: {generated_text!r}")
vLLM代码结构有非常清晰的类层次结构,整体的数据结构关系如下:
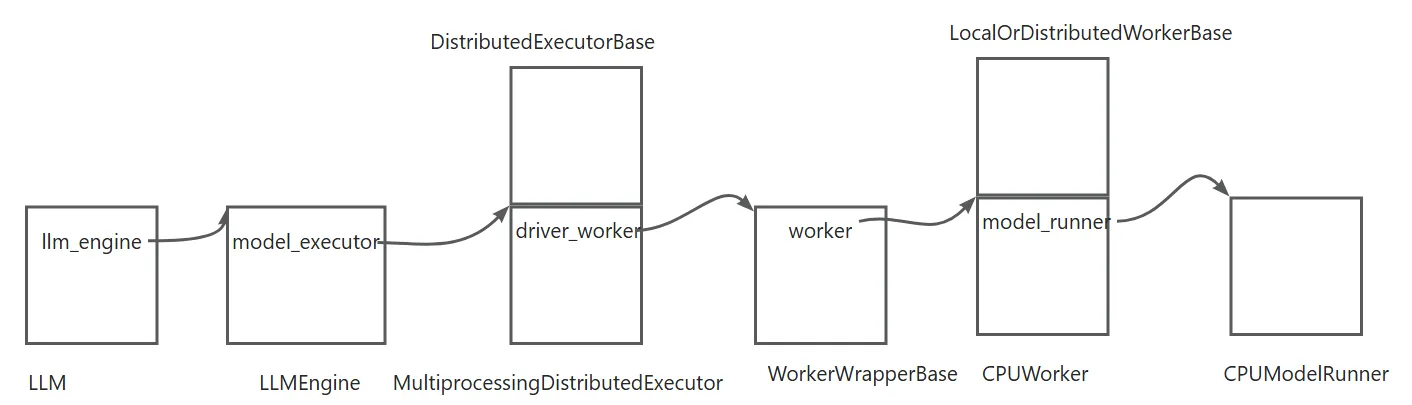
这里我们以V0分析,重在分析其各个类之间的关系,主要讨论核心的两个问题即LLM()创建模型引擎,以及通过llm.generate进行推理。本质就是加载模型和处理请求,本文只讨论整体结构,以CPU运行为例。
模型的加载
下面这个图展示了模型的加载流程,通过Executor、Worker层,最终由ModelRunner层开始加载模型。
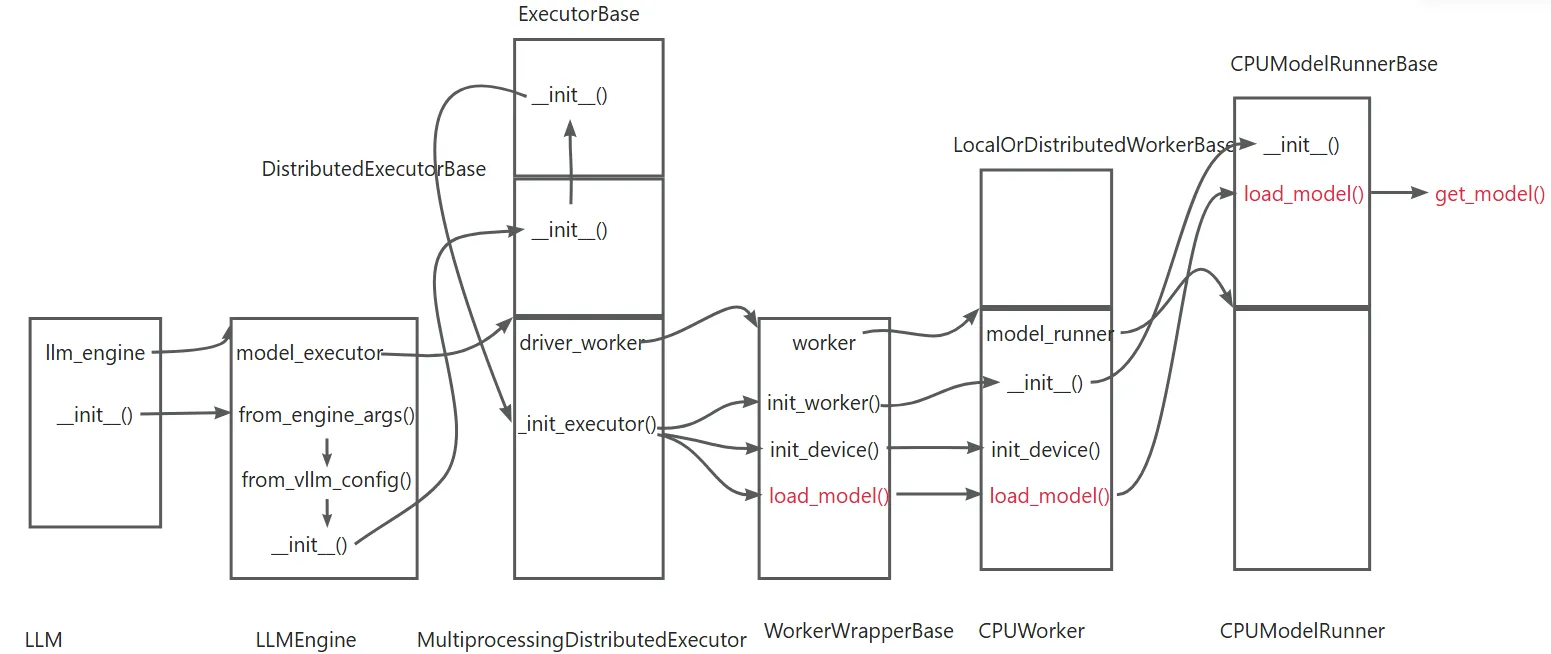
最终调用vllm/model/executor/model_loader/init.py文件中的get_model完成实际模型加载工作。
def get_model(*, vllm_config: VllmConfig) -> nn.Module:
loader = get_model_loader(vllm_config.load_config)
return loader.load_model(vllm_config=vllm_config)
这里loader默认情况下是DefaultModelLoader。其load_model函数如下:
def load_model(self, vllm_config: VllmConfig) -> nn.Module:
device_config = vllm_config.device_config
model_config = vllm_config.model_config
target_device = torch.device(device_config.device)
with set_default_torch_dtype(model_config.dtype):
with target_device:
model = _initialize_model(vllm_config=vllm_config)
weights_to_load = {name for name, _ in model.named_parameters()}
loaded_weights = model.load_weights(
self.get_all_weights(model_config, model))
self.counter_after_loading_weights = time.perf_counter()
logger.info(
"Loading weights took %.2f seconds",
self.counter_after_loading_weights -
self.counter_before_loading_weights)
# We only enable strict check for non-quantized models
# that have loaded weights tracking currently.
if model_config.quantization is None and loaded_weights is not None:
weights_not_loaded = weights_to_load - loaded_weights
if weights_not_loaded:
raise ValueError(
"Following weights were not initialized from "
f"checkpoint: {weights_not_loaded}")
_process_weights_after_loading(model, model_config, target_device)
return model.eval()
_initialize_model得到模型结构的class,并且调用模型的初始化函数,比如Qwen2ForCausalLM.init()函数。
def _initialize_model(
vllm_config: VllmConfig,
*,
prefix: str = "",
model_class: Optional[type[nn.Module]] = None,
) -> nn.Module:
"""Initialize a model with the given configurations."""
model_config = vllm_config.model_config
if model_class is None:
model_class, _ = get_model_architecture(model_config)
if vllm_config.quant_config is not None:
configure_quant_config(vllm_config.quant_config, model_class)
signatures = inspect.signature(model_class.__init__)
all_params = [param.name for param in signatures.parameters.values()]
if "vllm_config" in all_params and "prefix" in all_params:
# new-style model class
with set_current_vllm_config(vllm_config, check_compile=True):
return model_class(vllm_config=vllm_config, prefix=prefix)
...
model.load_weights则开始调用模型的函数加载权重。最终会调用到AutoWeightsLoader的load_wegiths函数。
def load_weights(self, weights: Iterable[Tuple[str,
torch.Tensor]]) -> Set[str]:
loader = AutoWeightsLoader(
self,
skip_prefixes=(["lm_head."]
if self.config.tie_word_embeddings else None),
)
return loader.load_weights(weights)
这里的wegiths是从 self.get_all_weights(model_config, model)) 这个函数获取的,get_all_wegiths从safetensors中加载权重。相关调用如下:
DefaultModelLoader.get_all_weights
-->self._get_weights_iterator
-->self._prepare_weights
-->safetensors_weights_iterator
safetensors_weights_iterator中打开文件。
def safetensors_weights_iterator(
hf_weights_files: List[str],
use_tqdm_on_load: bool,
) -> Generator[Tuple[str, torch.Tensor], None, None]:
"""Iterate over the weights in the model safetensor files."""
for st_file in tqdm(
hf_weights_files,
desc="Loading safetensors checkpoint shards",
disable=not enable_tqdm(use_tqdm_on_load),
bar_format=_BAR_FORMAT,
):
with safe_open(st_file, framework="pt") as f:
for name in f.keys(): # noqa: SIM118
param = f.get_tensor(name)
yield name, param
请求的处理
请求处理的过程如下:
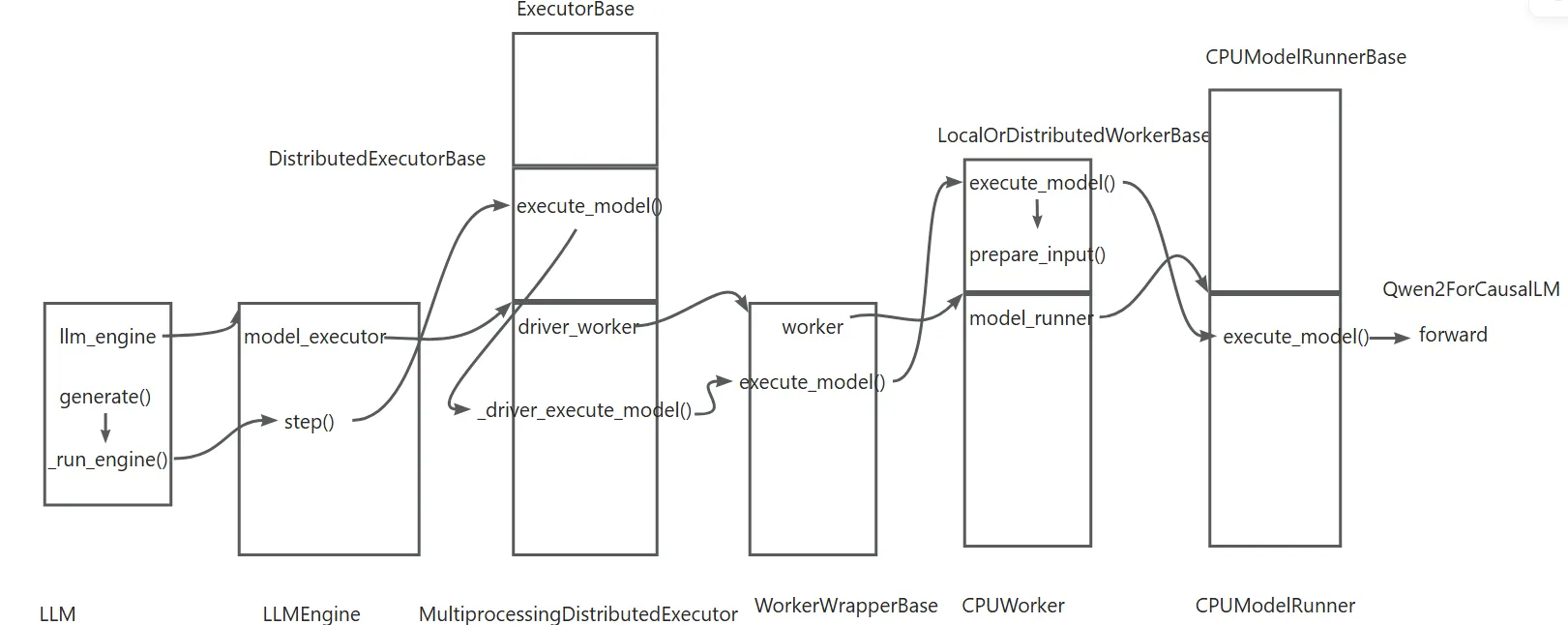
核心过程是在LLMEngine中的step函数。step函数注释很清晰,第一步将要处理的下一步的seq group找出来,第二步调用executor执行推理,第三步处理输出。
def step(self) -> List[Union[RequestOutput, PoolingRequestOutput]]:
"""Performs one decoding iteration and returns newly generated results.
.. figure:: https://i.imgur.com/sv2HssD.png
:alt: Overview of the step function
:align: center
Overview of the step function.
Details:
- Step 1: Schedules the sequences to be executed in the next
iteration and the token blocks to be swapped in/out/copy.
- Depending on the scheduling policy,
sequences may be `preempted/reordered`.
- A Sequence Group (SG) refer to a group of sequences
that are generated from the same prompt.
- Step 2: Calls the distributed executor to execute the model.
- Step 3: Processes the model output. This mainly includes:
- Decodes the relevant outputs.
- Updates the scheduled sequence groups with model outputs
based on its `sampling parameters` (`use_beam_search` or not).
- Frees the finished sequence groups.
- Finally, it creates and returns the newly generated results.
...
"""
...
# For llm_engine, there is no pipeline parallel support, so the engine
# used is always 0.
virtual_engine = 0
...
if not self._has_remaining_steps(
seq_group_metadata_list
) and not self._skip_scheduling_next_step:
# Schedule iteration
(seq_group_metadata_list, scheduler_outputs,
allow_async_output_proc
) = self.scheduler[virtual_engine].schedule()
ctx.seq_group_metadata_list = seq_group_metadata_list
ctx.scheduler_outputs = scheduler_outputs
...
if not scheduler_outputs.is_empty():
# Check if we have a cached last_output from the previous iteration.
# For supporting PP this is probably the best way to pass the
# sampled_token_ids, as a separate broadcast over all the PP stages
# will cause one virtual engine's microbatch to block the pipeline.
last_sampled_token_ids = \
self._get_last_sampled_token_ids(virtual_engine)
execute_model_req = ExecuteModelRequest(
seq_group_metadata_list=seq_group_metadata_list,
blocks_to_swap_in=scheduler_outputs.blocks_to_swap_in,
blocks_to_swap_out=scheduler_outputs.blocks_to_swap_out,
blocks_to_copy=scheduler_outputs.blocks_to_copy,
num_lookahead_slots=scheduler_outputs.num_lookahead_slots,
running_queue_size=scheduler_outputs.running_queue_size,
finished_requests_ids=finished_requests_ids,
# We use ExecuteModelRequest to pass the last sampled_token_ids
# to each of the non-last PP stages for in-place prepare_input.
last_sampled_token_ids=last_sampled_token_ids)
if allow_async_output_proc:
execute_model_req.async_callback = self.async_callbacks[
virtual_engine]
try:
outputs = self.model_executor.execute_model(
execute_model_req=execute_model_req)
self._skip_scheduling_next_step = False
except InputProcessingError as e:
...
# We need to do this here so that last step's sampled_token_ids can
# be passed to the next iteration for PP.
if self.scheduler_config.is_multi_step:
self._update_cached_scheduler_output(virtual_engine, outputs)
else:
...
# Finish the current step for all the sequence groups.
if self.scheduler_config.is_multi_step:
for seq_group in seq_group_metadata_list:
seq_group.finish_step()
if not self._has_remaining_steps(seq_group_metadata_list):
# clear the cache if we have finished all the steps.
if self.scheduler_config.is_multi_step:
self.cached_scheduler_outputs[0] = SchedulerOutputState()
# is_first_step_output is True only when the num_steps of all
# the sequences are 1. When the num_steps > 1,
# multi_step_model_runner does the first-step output append.
is_first_step_output: bool = False if not seq_group_metadata_list \
else seq_group_metadata_list[0].state.num_steps == 1
# Add results to the output_queue
ctx.append_output(outputs=outputs,
seq_group_metadata_list=seq_group_metadata_list,
scheduler_outputs=scheduler_outputs,
is_async=allow_async_output_proc,
is_last_step=True,
is_first_step_output=is_first_step_output)
...
else:
# Multi-step case
return ctx.request_outputs
if not self.has_unfinished_requests():
# Drain async postprocessor (if exists)
if len(ctx.output_queue) > 0:
self._process_model_outputs(ctx=ctx)
assert len(ctx.output_queue) == 0
# Stop the execute model loop in parallel workers until there are
# more requests to process. This avoids waiting indefinitely in
# torch.distributed ops which may otherwise timeout, and unblocks
# the RPC thread in the workers so that they can process any other
# queued control plane messages, such as add/remove lora adapters.
logger.debug("Stopping remote worker execution loop.")
self.model_executor.stop_remote_worker_execution_loop()
return ctx.request_outputs
这里我们只讨论推理的执行,该函数调用是调用下一层(executor)的execute_model,参数是一个ExecuteModelRequest,其中的seq_group_metadata_list保存了seq group的数据信息。
outputs = self.model_executor.execute_model(
execute_model_req=execute_model_req)
executor只是中间商,会调用Worker的execute_model函数。在这个里面会调用Worker的prepare_input来准备模型的输入,然后有了输入调用Runner的execute_model开始完成一次推理过程。
class LocalOrDistributedWorkerBase(WorkerBase):
...
def execute_model(
self,
execute_model_req: Optional[ExecuteModelRequest] = None,
) -> Optional[List[SamplerOutput]]:
"""Executes at least one model step on the given sequences, unless no
sequences are provided."""
start_time = time.perf_counter()
inputs = self.prepare_input(execute_model_req)
if inputs is None:
return None
model_input, worker_input, kwargs = inputs
num_steps = worker_input.num_steps
if (execute_model_req is not None and execute_model_req.spec_step_idx):
kwargs["spec_step_idx"] = execute_model_req.spec_step_idx
self.execute_worker(worker_input)
# If there is no input, we don't need to execute the model.
if worker_input.num_seq_groups == 0:
return []
intermediate_tensors = None
orig_model_execute_time = 0.0
...
output = self.model_runner.execute_model(
model_input=model_input,
kv_caches=self.kv_cache[worker_input.virtual_engine]
if self.kv_cache is not None else None,
intermediate_tensors=intermediate_tensors,
num_steps=num_steps,
**kwargs,
)
model_execute_time = time.perf_counter() - start_time
if not get_pp_group().is_last_rank:
# output is IntermediateTensors
assert isinstance(output, IntermediateTensors)
if (self.observability_config is not None
and self.observability_config.collect_model_execute_time):
output.tensors["model_execute_time"] = torch.tensor(
model_execute_time + orig_model_execute_time)
get_pp_group().send_tensor_dict(output.tensors,
all_gather_group=get_tp_group())
return [None]
if (self.observability_config is not None
and self.observability_config.collect_model_execute_time
and output is not None):
for o in output:
o.model_execute_time = (orig_model_execute_time +
model_execute_time)
# output is List[SamplerOutput]
return output
在Runner(这里是CPUModelRunner)中的execute_model会调用模型的forward函数。这里调用set_forward_context是将attention的数据与本次推理管理起来。随后调用model_executable(forward)。 这里就到了实际模型(比如Qwen2ForCausalLM)的forward函数。
def execute_model(
self,
model_input: ModelInputForCPUWithSamplingMetadata,
kv_caches: List[torch.Tensor],
intermediate_tensors: Optional[IntermediateTensors] = None,
num_steps: int = 1,
previous_hidden_states: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
) -> Optional[List[SamplerOutput]]:
...
model_executable = self.model
...
with set_forward_context(model_input.attn_metadata, self.vllm_config,
model_input.virtual_engine):
hidden_states = model_executable(
input_ids=model_input.input_tokens,
positions=model_input.input_positions,
intermediate_tensors=intermediate_tensors,
**execute_model_kwargs,
**multimodal_kwargs,
)
# Compute the logits.
logits = self.model.compute_logits(hidden_states,
model_input.sampling_metadata)
# Only perform sampling in the driver worker.
if not self.is_driver_worker:
return []
# Sample the next token.
output = self.model.sample(
logits=logits,
sampling_metadata=model_input.sampling_metadata,
)
if self.return_hidden_states:
# we only need to pass hidden states of most recent token
if model_input.is_prompt:
output.prefill_hidden_states = hidden_states
output.hidden_states = hidden_states
return [output]
blog comments powered by Disqus