KVM async page fault
apf introduction
The qemu/kvm VM’s physical memory is the virtual memory of qemu process. When the virtual memory of qemu has been commit and is setup with physical memory the host can swap out this physical memory. When the guest vcpu access memory swapped out by host its execution is suspended until memory is swapped back. Asynchronous page fault is a way to try and use guest vcpu more efficiently by allowing it to execute other tasks while page is brought back into memory[1]. Following give a summary of these processes.
-
page fault when the EPT page table is not setup
1. VMEXIT 2. kvm_mmu_page_fault() 3. gfn_to_pfn() 4. get_user_pages_unlocked() no previously mapped page and no swap entry found empty page is allocated 5. page is added into shadow/nested page table -
page fault when the physical memory is swapped out(without apf)
1. VMEXIT 2. kvm_mmu_page_fault() 3. gfn_to_pfn() 4. get_user_pages_unlocked() swap entry is found page swap-in process is initiated vcpu thread goes to sleep until page is swapped in -
page fault when the phycial memory is swapped out(with apf)
1. VMEXIT 2. kvm_mmu_page_fault() 3. gfn_to_pfn() 4. get_user_pages_nowait() 5. gup is done by dedicated thread, inject 'page not present' exception to guest 6. guest puts process A(which caused this page fault) to sleep and schedule another process 7. page is swapped in, inject 'page ready' exception to guest 8. guest can schedule process A back to run on vcpu
Following shows the process of kvm async page fault process.[2]
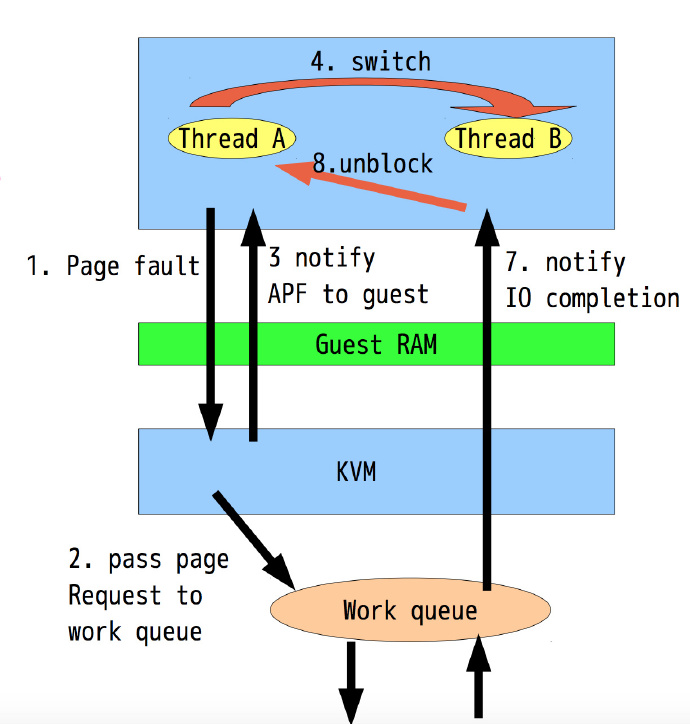
From description we know that kvm apf need the guest do something, such as recognize the apf ‘page not present’ and ‘page ready’ exception, and also the para guest should hook the exception to process these two new exception. apf contains following steps.
1. the guest should be initialized to process the new exception
2. kvm page fault handler should recognize the swapped out case and initialize a work to swap in the page, inject a 'page not present' to guest
3. the guest receive this exception and schedule another process to run
4. when the page caused page fault in step 2 has been swapped in, the kvm inject a 'page ready' exception to guest
5. the guest can do schedule to run process that was blocked by page fault in step 2
Next part I will discuss the code in above process.
detail of apf
para guest initialization when startup
commit: KVM paravirt: Add async PF initialization to PV guest.
Here we can see, the apf is enabled default and can be disabled with the ‘no-kvmapf’ parameter in kernel command line.
Every CPU has a per-cpu vairable named ‘apf_reason’, it is defined as following:
+struct kvm_vcpu_pv_apf_data {
+ __u32 reason;
+ __u8 pad[60];
+ __u32 enabled;
+};
The ‘reason’ here is the exception of apf, can be ‘KVM_PV_REASON_PAGE_NOT_PRESENT’(1) or ‘KVM_PV_REASON_PAGE_READY’(2), the ‘enabled’ indicates the status of apf. When
If the kvm support apf, the ‘KVM_CPUID_FEATURES’ cpuid leaf has ‘KVM_FEATURE_ASYNC_PF’ feature, When the guest detect this feature, it writes the ‘afp_reason’s physical address to msr ‘MSR_KVM_ASYNC_PF_EN’.
+void __cpuinit kvm_guest_cpu_init(void)
+{
+ if (!kvm_para_available())
+ return;
+
+ if (kvm_para_has_feature(KVM_FEATURE_ASYNC_PF) && kvmapf) {
+ u64 pa = __pa(&__get_cpu_var(apf_reason));
+
+ wrmsrl(MSR_KVM_ASYNC_PF_EN, pa | KVM_ASYNC_PF_ENABLED);
+ __get_cpu_var(apf_reason).enabled = 1;
+ printk(KERN_INFO"KVM setup async PF for cpu %d\n",
+ smp_processor_id());
+ }
+}
guest process the apf exception
commit: KVM: Handle async PF in a guest
In the initialization, it sets the trap_init to ‘kvm_apf_trap_init’, and in the later function it set the ‘14’ gate’s(page fault) handler to ‘async_page_fault’.
+static void __init kvm_apf_trap_init(void)
+{
+ set_intr_gate(14, &async_page_fault);
+}
The ‘async_page_fault’ calls ‘do_async_page_fault’. The later function first read the ‘
+u32 kvm_read_and_reset_pf_reason(void)
+{
+ u32 reason = 0;
+
+ if (__get_cpu_var(apf_reason).enabled) {
+ reason = __get_cpu_var(apf_reason).reason;
+ __get_cpu_var(apf_reason).reason = 0;
+ }
+
+ return reason;
+}
+dotraplinkage void __kprobes
+do_async_page_fault(struct pt_regs *regs, unsigned long error_code)
+{
+ switch (kvm_read_and_reset_pf_reason()) {
+ default:
+ do_page_fault(regs, error_code);
+ break;
+ case KVM_PV_REASON_PAGE_NOT_PRESENT:
+ /* page is swapped out by the host. */
+ kvm_async_pf_task_wait((u32)read_cr2());
+ break;
+ case KVM_PV_REASON_PAGE_READY:
+ kvm_async_pf_task_wake((u32)read_cr2());
+ break;
+ }
+}
+
The apf reason is writen to ‘apf_reason.reason’ field by kvm and the guest can read it out. When apf reason is ‘KVM_PV_REASON_PAGE_NOT_PRESENT’ it calls ‘kvm_async_pf_task_wait’ adds current process to a sleep list and reschedule. When the guest receive ‘KVM_PV_REASON_PAGE_READY’ it calls ‘kvm_async_pf_task_wake’ to wakeup the sleep process.
kvm support the apf cpuid feature and msr
commit: KVM: Add PV MSR to enable asynchronous page faults delivery
As we discussed, the kvm should support the ‘KVM_FEATURE_ASYNC_PF’ cpuid and msr ‘MSR_KVM_ASYNC_PF_EN’.
When the guest write to msr ‘MSR_KVM_ASYNC_PF_EN’ the kvm module calls ‘kvm_pv_enable_async_pf’. In this function it saves the per-cpu variable ‘apf_reason’ to ‘vcpu’s arch field ‘apf.msr_val’. ‘kvm_gfn_to_hva_cache_init’ creates a ‘cache’ for gpa to hva so that the kvm can write data to guest more efficiently.
+static int kvm_pv_enable_async_pf(struct kvm_vcpu *vcpu, u64 data)
+{
+ gpa_t gpa = data & ~0x3f;
+
+ /* Bits 1:5 are resrved, Should be zero */
+ if (data & 0x3e)
+ return 1;
+
+ vcpu->arch.apf.msr_val = data;
+
+ if (!(data & KVM_ASYNC_PF_ENABLED)) {
+ kvm_clear_async_pf_completion_queue(vcpu);
+ kvm_async_pf_hash_reset(vcpu);
+ return 0;
+ }
+
+ if (kvm_gfn_to_hva_cache_init(vcpu->kvm, &vcpu->arch.apf.data, gpa))
+ return 1;
+
+ kvm_async_pf_wakeup_all(vcpu);
+ return 0;
+}
+
kvm do the apf work
There are two commit with this part. commit: KVM: Halt vcpu if page it tries to access is swapped out this commit setup the framework of apf.
commit: KVM: Inject asynchronous page fault into a PV guest if page is swapped out this commit do the final work
Let’s first look at the first commit.
Every apf work is presented by the following structure.
+struct kvm_async_pf {
+ struct work_struct work;
+ struct list_head link;
+ struct list_head queue;
+ struct kvm_vcpu *vcpu;
+ struct mm_struct *mm;
+ gva_t gva;
+ unsigned long addr;
+ struct kvm_arch_async_pf arch;
+ struct page *page;
+ bool done;
+};
The apf occurs in page fault process, the function is ‘tdp_page_fault’. So this commit add the call to a new function ‘try_async_pf’.
+static bool try_async_pf(struct kvm_vcpu *vcpu, gfn_t gfn, gva_t gva,
+ pfn_t *pfn)
+{
+ bool async;
+
+ *pfn = gfn_to_pfn_async(vcpu->kvm, gfn, &async);
+
+ if (!async)
+ return false; /* *pfn has correct page already */
+
+ put_page(pfn_to_page(*pfn));
+
+ if (can_do_async_pf(vcpu)) {
+ trace_kvm_try_async_get_page(async, *pfn);
+ if (kvm_find_async_pf_gfn(vcpu, gfn)) {
+ trace_kvm_async_pf_doublefault(gva, gfn);
+ kvm_make_request(KVM_REQ_APF_HALT, vcpu);
+ return true;
+ } else if (kvm_arch_setup_async_pf(vcpu, gva, gfn))
+ return true;
+ }
+
+ *pfn = gfn_to_pfn(vcpu->kvm, gfn);
+
+ return false;
+}
+int kvm_setup_async_pf(struct kvm_vcpu *vcpu, gva_t gva, gfn_t gfn,
+ struct kvm_arch_async_pf *arch)
+{
+ struct kvm_async_pf *work;
+
+ if (vcpu->async_pf.queued >= ASYNC_PF_PER_VCPU)
+ return 0;
+
+ /* setup delayed work */
+
+ /*
+ * do alloc nowait since if we are going to sleep anyway we
+ * may as well sleep faulting in page
+ */
+ work = kmem_cache_zalloc(async_pf_cache, GFP_NOWAIT);
+ if (!work)
+ return 0;
+
+ work->page = NULL;
+ work->done = false;
+ work->vcpu = vcpu;
+ work->gva = gva;
+ work->addr = gfn_to_hva(vcpu->kvm, gfn);
+ work->arch = *arch;
+ work->mm = current->mm;
+ atomic_inc(&work->mm->mm_count);
+ kvm_get_kvm(work->vcpu->kvm);
+
+ /* this can't really happen otherwise gfn_to_pfn_async
+ would succeed */
+ if (unlikely(kvm_is_error_hva(work->addr)))
+ goto retry_sync;
+
+ INIT_WORK(&work->work, async_pf_execute);
+ if (!schedule_work(&work->work))
+ goto retry_sync;
+
+ list_add_tail(&work->queue, &vcpu->async_pf.queue);
+ vcpu->async_pf.queued++;
+ kvm_arch_async_page_not_present(vcpu, work);
+ return 1;
+retry_sync:
+ kvm_put_kvm(work->vcpu->kvm);
+ mmdrop(work->mm);
+ kmem_cache_free(async_pf_cache, work);
+ return 0;
+}
If the kvm can do apf, it calls ‘kvm_setup_async_pf’(called by ‘kvm_arch_setup_async_pf’) to setup a ‘work queue’ and calls ‘kvm_arch_async_page_not_present’ to notify the guest. As this commit just setups the apf framework, the ‘kvm_arch_async_page_not_present’ doesn’t inject interrupt.
‘kvm_setup_async_pf’ initializes a ‘work_struct’ and its function is ‘async_pf_execute’. ‘async_pf_execute’ swaps in the fault page.
Then in the ‘__vcpu_run’ when the guest VMEXIT, it calls ‘kvm_check_async_pf_completion’ to check whether the apf work is done. This is the first version of apf, called ‘batch mechanism’. Commit KVM: async_pf: Provide additional direct page notification add a Config ‘KVM_ASYNC_PF_SYNC’. When this selected, the ‘kvm’ will notify the guest directly.
commit: KVM: Inject asynchronous page fault into a PV guest if page is swapped out is easy to understand.
Following is the core, when the page not present, the kvm can halt the vcpu or inject ‘KVM_PV_REASON_PAGE_NOT_PRESENT’ to guest. When the async page is ready, the kvm inject ‘KVM_ASYNC_PF_ENABLED’ to guest.
void kvm_arch_async_page_not_present(struct kvm_vcpu *vcpu,
struct kvm_async_pf *work)
{
- trace_kvm_async_pf_not_present(work->gva);
-
- kvm_make_request(KVM_REQ_APF_HALT, vcpu);
+ trace_kvm_async_pf_not_present(work->arch.token, work->gva);
kvm_add_async_pf_gfn(vcpu, work->arch.gfn);
+
+ if (!(vcpu->arch.apf.msr_val & KVM_ASYNC_PF_ENABLED) ||
+ kvm_x86_ops->get_cpl(vcpu) == 0)
+ kvm_make_request(KVM_REQ_APF_HALT, vcpu);
+ else if (!apf_put_user(vcpu, KVM_PV_REASON_PAGE_NOT_PRESENT)) {
+ vcpu->arch.fault.error_code = 0;
+ vcpu->arch.fault.address = work->arch.token;
+ kvm_inject_page_fault(vcpu);
+ }
}
void kvm_arch_async_page_present(struct kvm_vcpu *vcpu,
struct kvm_async_pf *work)
{
- trace_kvm_async_pf_ready(work->gva);
- kvm_del_async_pf_gfn(vcpu, work->arch.gfn);
+ trace_kvm_async_pf_ready(work->arch.token, work->gva);
+ if (is_error_page(work->page))
+ work->arch.token = ~0; /* broadcast wakeup */
+ else
+ kvm_del_async_pf_gfn(vcpu, work->arch.gfn);
+
+ if ((vcpu->arch.apf.msr_val & KVM_ASYNC_PF_ENABLED) &&
+ !apf_put_user(vcpu, KVM_PV_REASON_PAGE_READY)) {
+ vcpu->arch.fault.error_code = 0;
+ vcpu->arch.fault.address = work->arch.token;
+ kvm_inject_page_fault(vcpu);
+ }
+}
Reference
blog comments powered by Disqus